Lighting is the most important component for indoor plants. At first, you need to understand the light needs of plants, whether they are small succulents or tropical plants, which is critical for success. Plants use light to undergo photosynthesis, enabling flowers and plants to grow and bloom. For indoor plants, this may not be necessary. Because artificial lighting takes over in that place. So we need to know when and how to use the options at your disposal to create the best lighting for indoor plants.

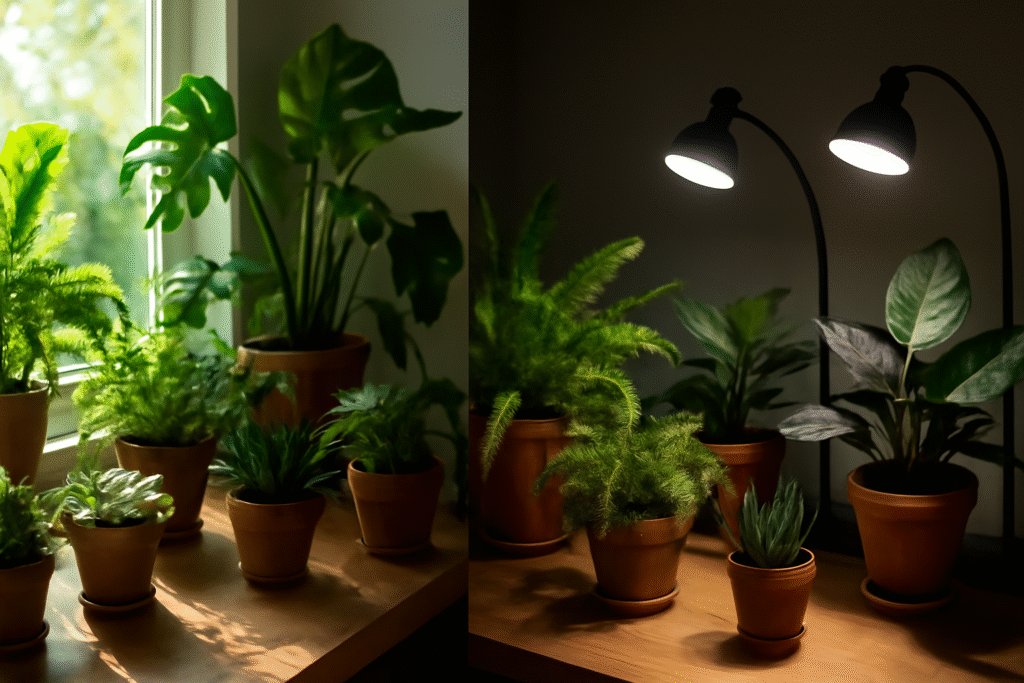
Sunlight vs. Artificial Light: Which Works Better?
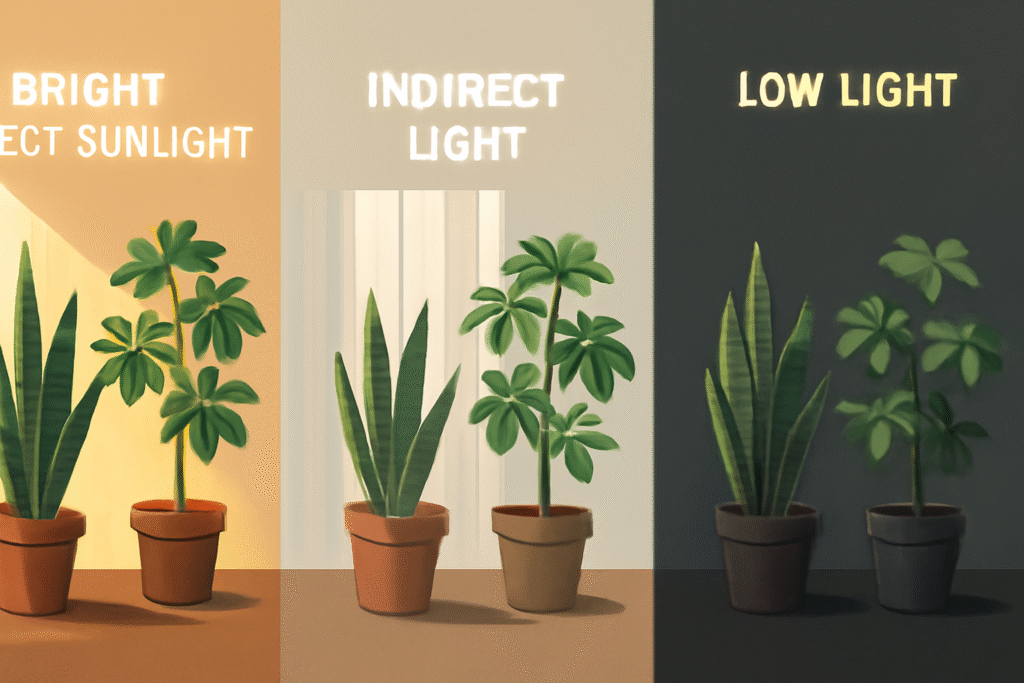
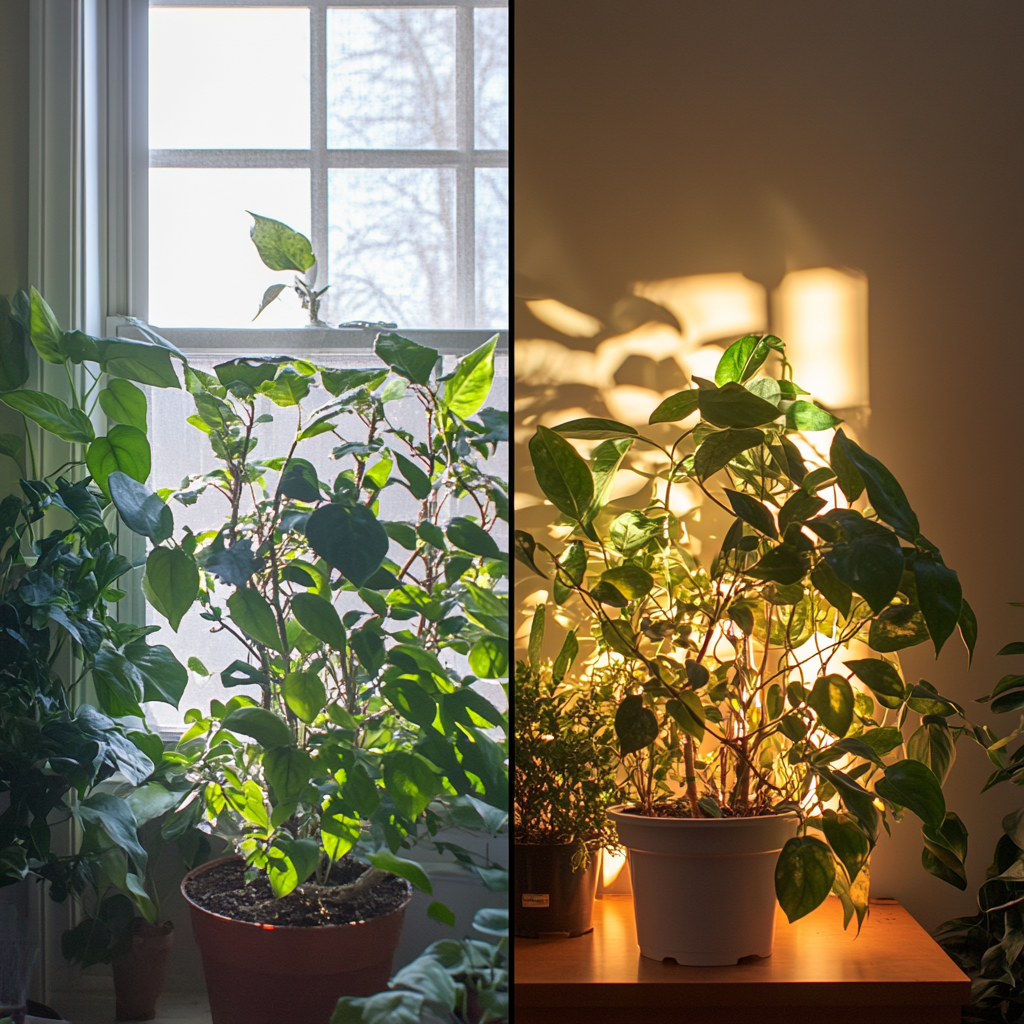
If the question is about giving light to your indoor plants, then natural sunlight will be the best. Sunlight contains the entire spectrum of light, which is required for photosynthesis. If your home has larger windows receiving either direct or indirect sunlight, you may not need artificial lighting for a variety of plants indoors. But not every home can have the proper light for every type of plant. Whereas some plants get scorched by too much direct sun, others may not get enough to become stunted in growth in leaves.
The main reasons for using artificial lighting in the home are when there is very limited natural light available, or when trying to duplicate seasonal light for certain plants throughout the whole year. Artificial lighting is good when the sunlight becomes inconsistent due to a change in the season. It provides a controlled and steady supply of light with the use of artificial lights. This is especially helpful when the sun is infrequent in a room. You have to know when to use natural light and when to replace it with artificial lighting.

Top Artificial Light Options
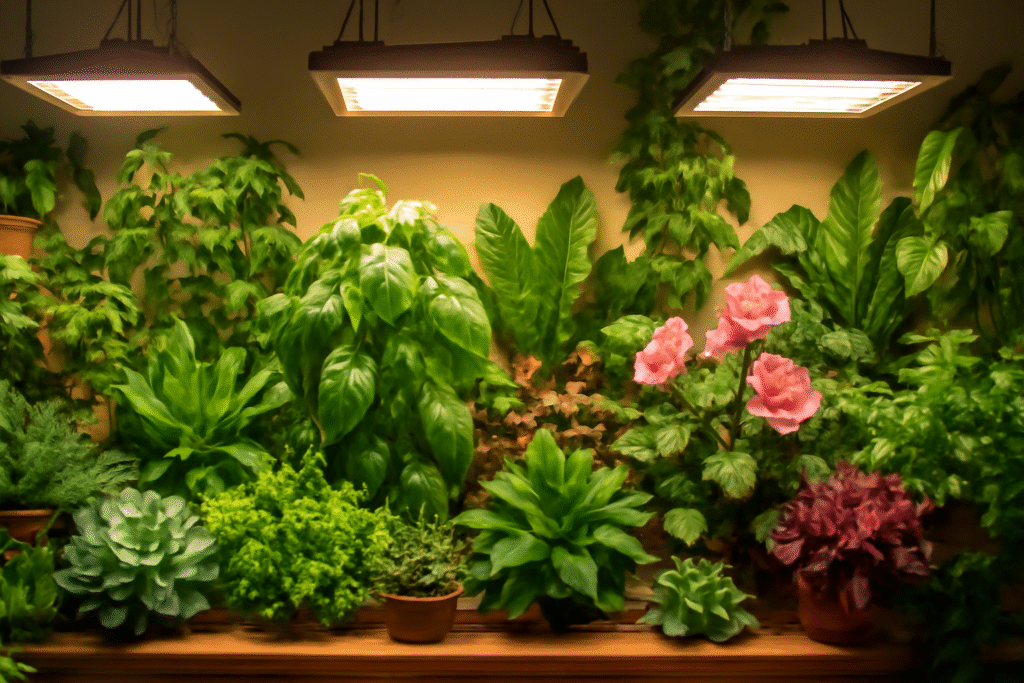
When natural is not enough, several artificial lighting options are available for indoor plants. Each of these has disadvantages and advantages. The right light to be used would depend upon the needs of your plant and your preference.
1. LED Lights
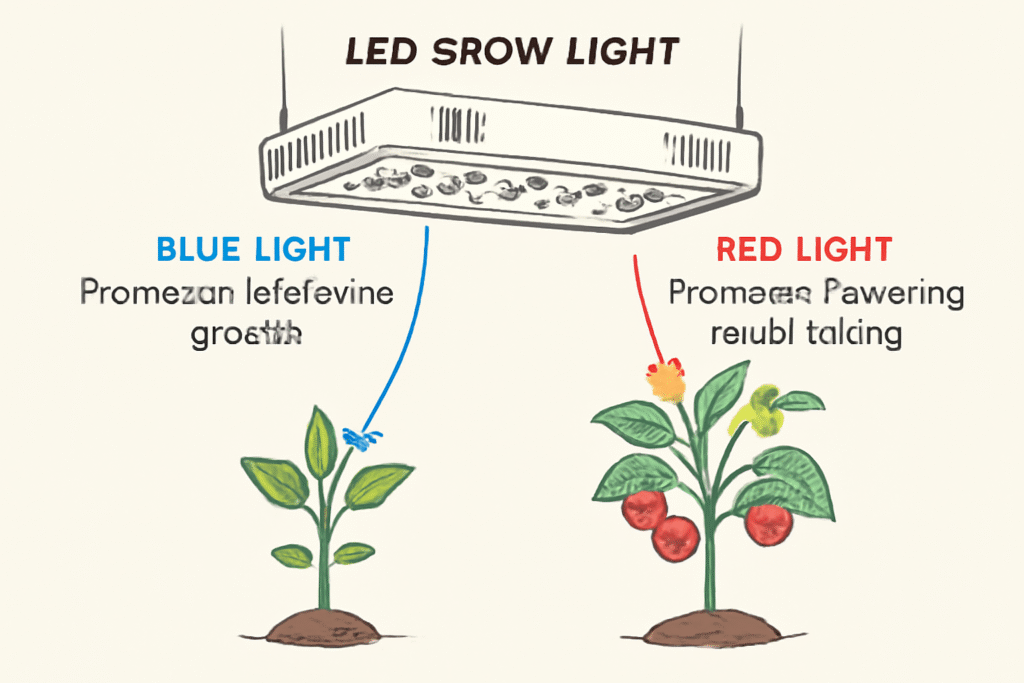
LED lights have gained increasing popularity in indoor gardening due to their efficiency and long life. They create very little heat, which means they can be placed closer to plants without the risk of them burning. LED lights do come in full-spectrum, near natural sunlight. Thus, they work great for a wide range of plants. They have but one downside—the initial investment, which can be a bit higher than other light sources. This light is very energy-saving.

2. Fluorescent Lights
They operate more economically and work quite well with indoor plants, especially those that require minimal light, such as herbs or leafy greens, or low-light houseplants such as pothos. Fluorescent lights also produce much less heat than regular incandescent bulbs.They make it safe for plants at closer distances. However, they do offer an incomplete spectrum, which may eventually hinder plant development.
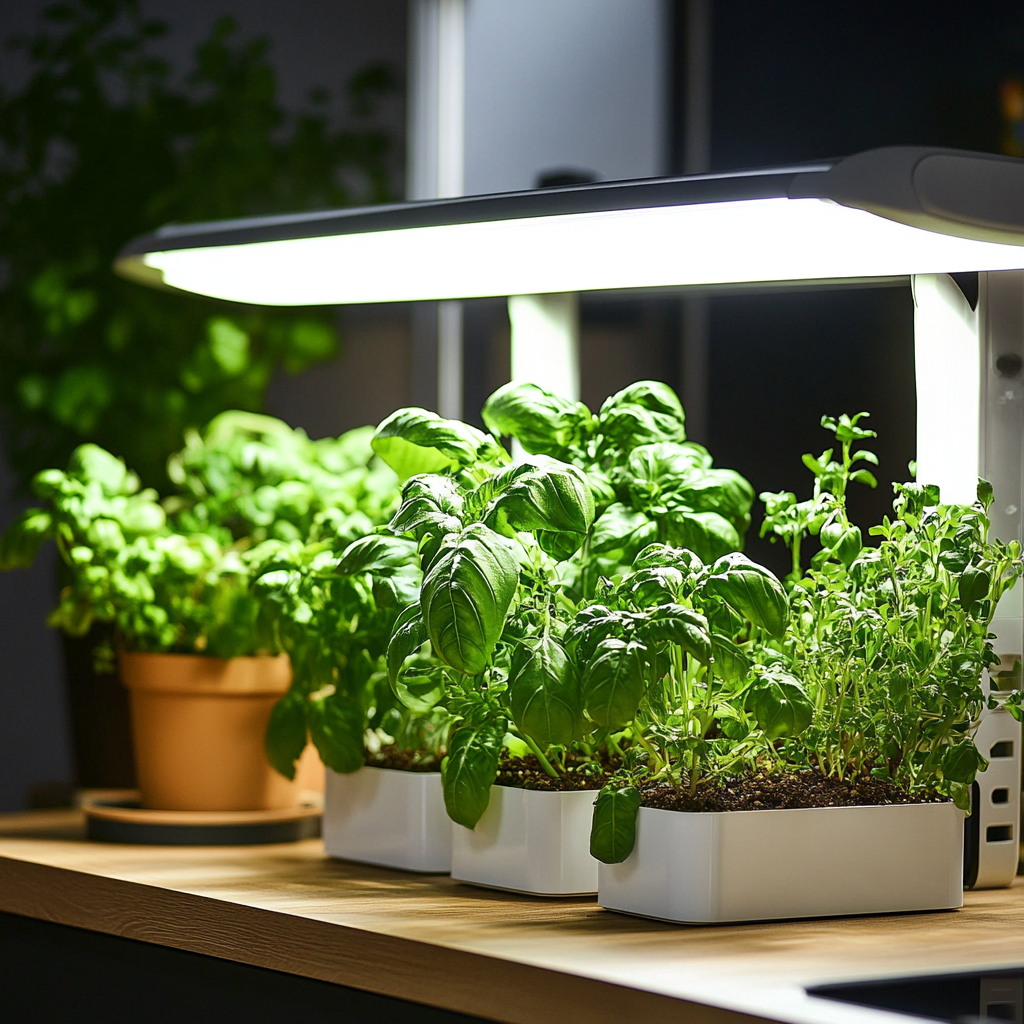

3. Grow Lights
Grow lights are specially useful for plant development. The forms of this light range from tubes to compact bulbs, which will give different light spectrums intended for the different plant types. Grow lights can be adjusted in their intensity and are great for indoor gardeners. This is good for looking to grow more light-hungry plants, such as flowering varieties or even tropical species. While grow lights can give you great flexibility, they tend to be more expensive and sometimes take some experimentation to get just the right setup for your plants.

How to Adjust and Measure Lighting for Your Plants
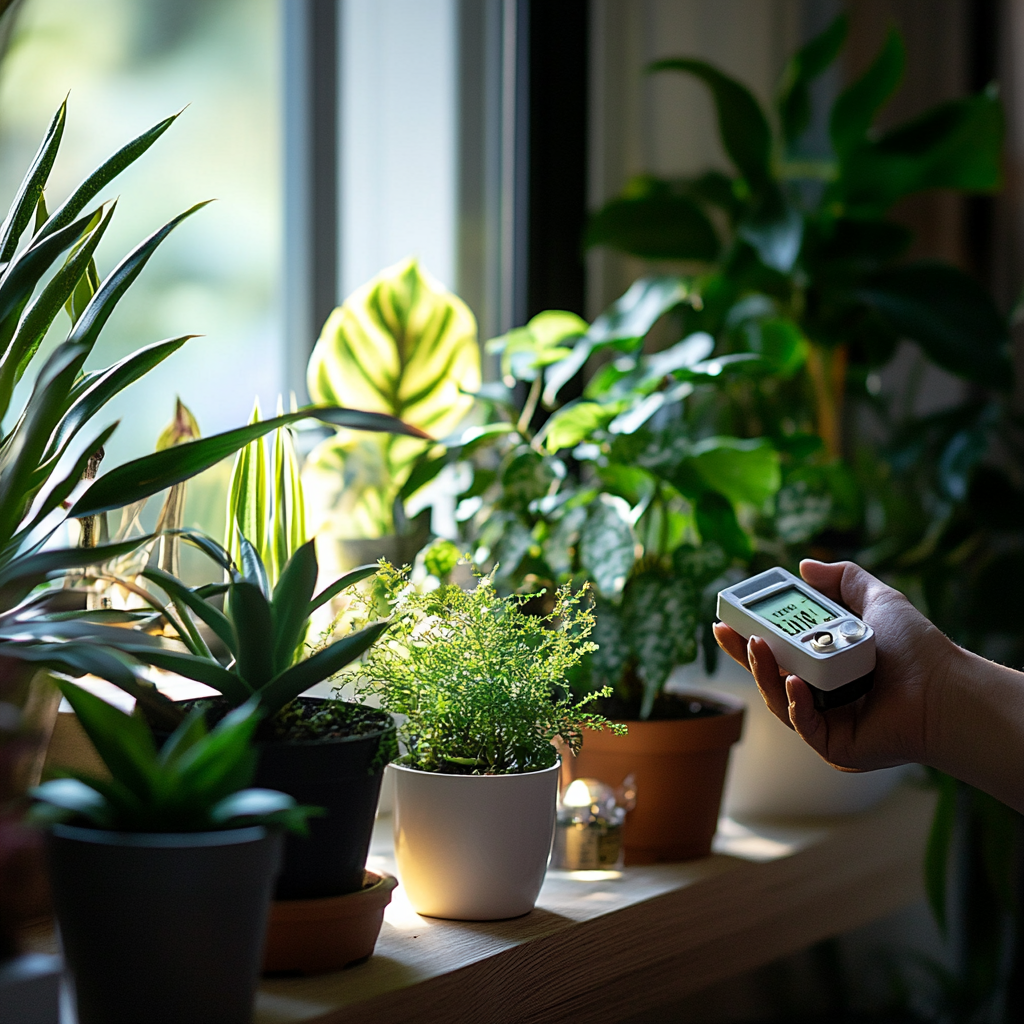
You have to know how much light is needed for the health of your plants. Too little light causes leggy growth and poor health, and high light can cause burning. There are meters to aid in measuring the light intensity within your home. These meters will let you know about how much light different areas of your home receive.
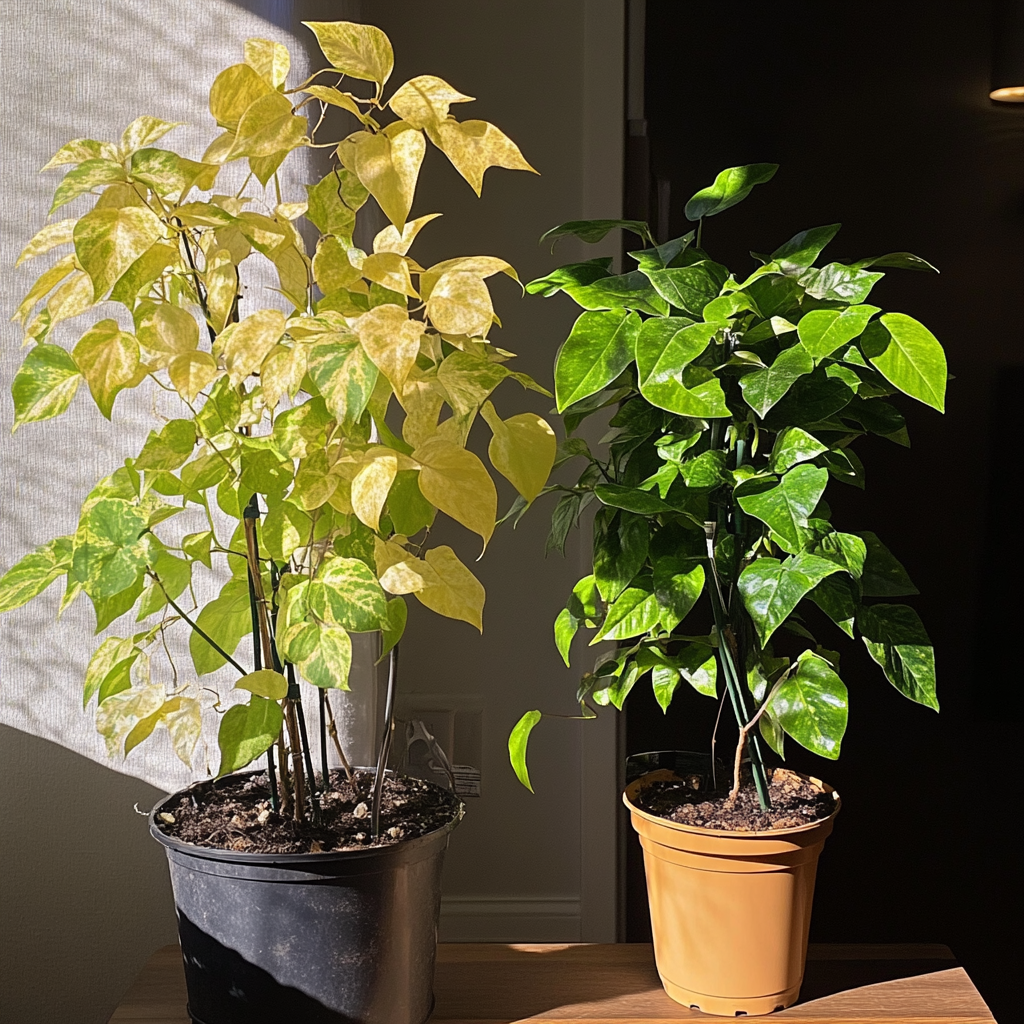
Besides measuring, you also need to observe your plants very keenly. If the plant is getting too much light, the leaves often become yellow or scorched. Sometimes, when plants show leggy growth and pale foliage, that is usually a sign of an absence of light. If you are growing under artificial lights, make sure the lights are at the right distance. Most plants are comfortable at about 6 to 12 inches away from the light source, though this is dependent on both the plant and the type of light one uses.

Common Problems in Indoor Plant Lighting and How to Solve the Problem
Even with the proper lighting system in place, you are likely to encounter some of the more general problems with lighting. The most frequent issue refers to the uneven distribution of light. Solve this by rotating your plants every few days so they all get to have equal exposure to light.
Another problem is light burn. This happens when plants get too much strong light, usually from an artificial source positioned too close to the leaves. This can be solved by just moving the light farther away from plants.
If you are low on light, you will probably want to place them closer to a window or use some sort of artificial light source. The balance of light for growing your plants indoors is quite an important factor in the overall health of the plants. Knowing what the plant wants will thus be key, and adjustments will be made according to their need.